David Silver / UCL Course on RL
https://www.davidsilver.uk/teaching/
Teaching - David Silver
www.davidsilver.uk
- Reinforcement Learning (RL) is concerned with goal-directed learning and decision-making.
- In RL, an agent learns from experiences it gains by interacting with the environment. In Supervised Learning we cannot affect the environment.
- In RL, rewards are often delayed in time and the agent tries to maximize a long-term goal. For example, one may need to make seemingly suboptimal moves to reach a winning position in a game.
- An agent interacts with the environment via states, actions and rewards.
- RL은 상호작용으로부터 배우는 목표 지향적인 학습에 초점을 맞춘 방법임.
- 시행착오, 지연된 보상
- RL의 구성 요소 : 정책, 보상 신호, 가치 함수, 모델
- 정책의 공간에서 효율적인 탐색이 이루어지기 위해서는 가치 함수가 중요함! <- 가치 함수 사용한다는 점에서 진화적 방법과 구별됨.
Reward Hypothesis
All goals can be described by the maximisation of expected cumulative reward.
Sequential Decision Making
Goal : select actions to maximise total future reward
The agent selects actions / The environment selects observations and rewards



현재 state s의 가치를 판단하는 함수 <- 누적 보상의 기댓값으로 판단.
현재 state S_t의 가치로 어떤 행동 A_t를 취할 지 선택함.

아직도 time step t의 순서를 모르겠음
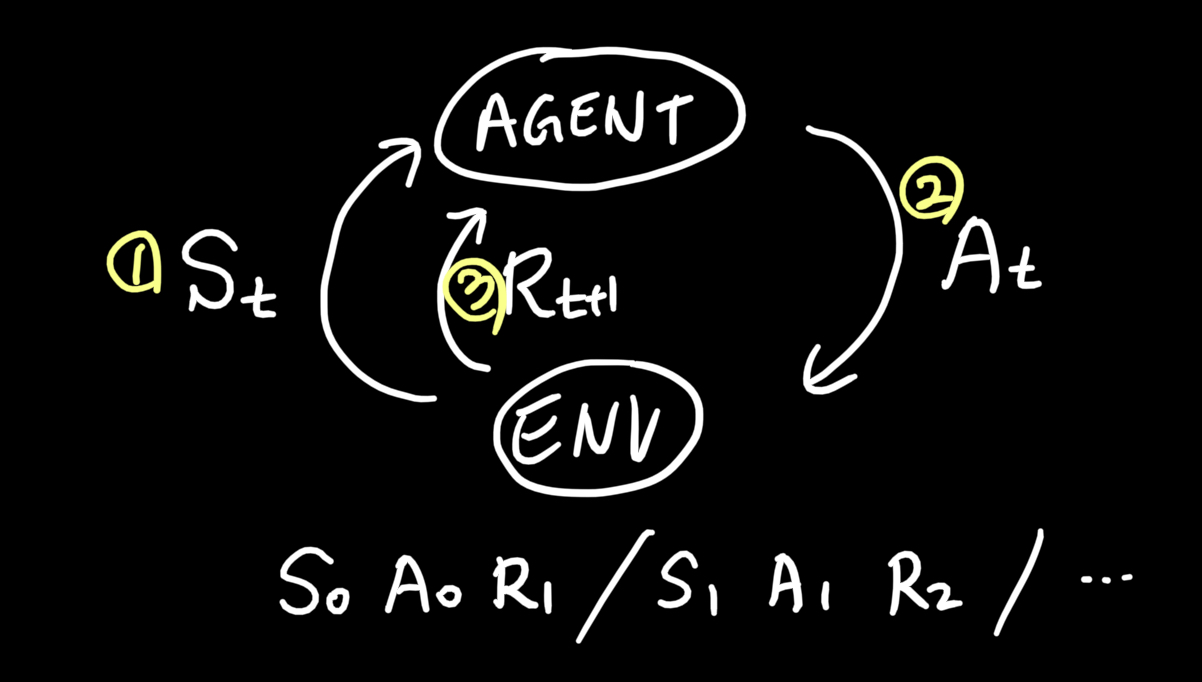
이게 맞는 듯
'Reinforcement Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| MDP (3) | 2023.01.21 |
|---|---|
| dennybritz/reinforcement-learning (0) | 2023.01.21 |
